Rethinking Classification and Localization for Object Detection
1. Abstract
-
투 트랙(classification, box regression)으로 진행되는 2개의 Head 구조의 진행방식에 대한 이해를 높이기 위해 진행.
-
결과적으로, fully-connected head(fc-head)가 classification task에 적합했고, convolution head(conv-head)가 localization task에 적합했다.
-
게다가 fc-head가 conv-head에 비해 spatial sensitivity를 더 가지고 있기에, 객체의 일부와 전체를 구분할 수 있었다. 이러한 발견들을 기반으로, Double-Head 방법(fully connected head는 classification에 초점을, convolution head는 bounding box regression에 초점을 두는)을 제안한다.
2. Introduction
-
대다수의 two-stage object detection 기법들은 classification과 bounding box regression의 head를 공유하고 있다. 대표적으로 2개의 다른 head structure가 사용된다. Faster R-CNN에서 convolution head는 single level feature map에서 사용되는 반면에, FPN에서 fully connected head는 multiple level feature map에서 사용된다.
-
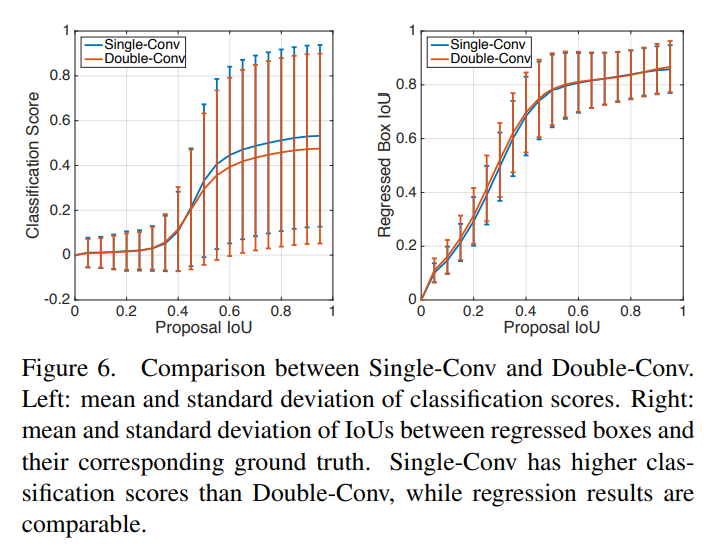
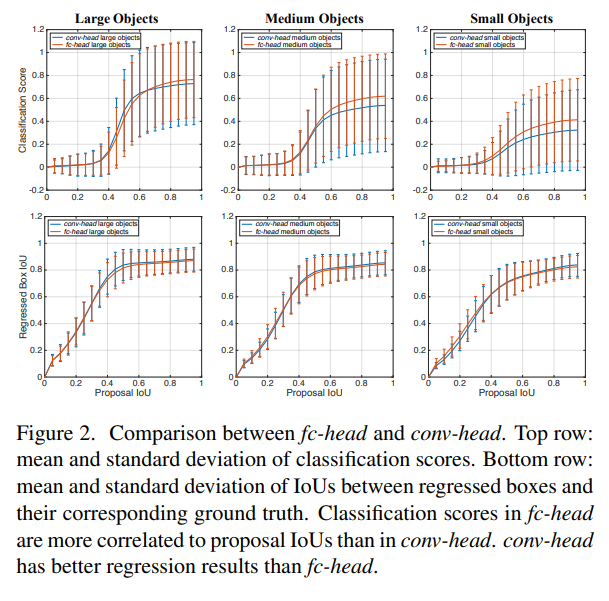
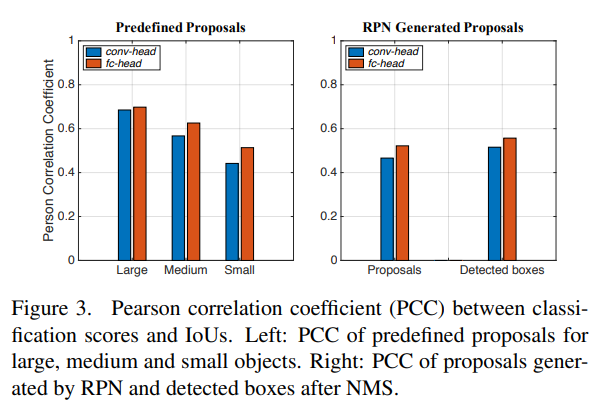
본 논문에서는 위와 같이 2개의 task에 따른 2개의 head 구조 사이의 이해성의 부족을 돕고자, 철처하게 fully-connected head와 convolution head를 비교 분석했다. fc-head는 ground truth box와 proposal 사이의 IoU 상관관계에서 더 많은 classification 점수를 가지는 결과를 토대로, classification task에 더욱 적합하다는 것을 알 수 있었다. 반면에, conv-head는 bounding box regression을 더욱 정확하게 제공해준다는 것을 알 수 있었다.
-
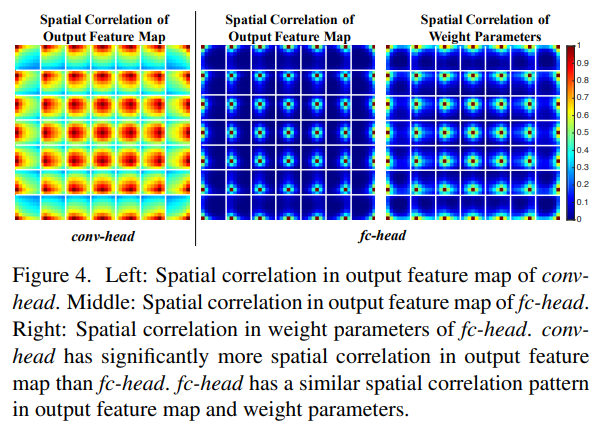
이와 같은 이유를, fc-head가 서로 다른 proposal의 다른 파라미터들을 가지고 있기에 공간적으로 sensitive하고, 반대로 conv-head는 모든 부분에서 convolution kernels를 공유하고 있기 때문이라고 여겼다. 이를 입증하기 위해, 두 가지 head의 output feature map을 검증하고 fc-head가 더욱 공간적으로 sensitive한지를 확인해봤다. 그 결과, fc-head가 complete object와 part of an object 사이를 더 잘 구분할 수 있었고, conv-head는 전체 객체들의 예측을 robust하게 하였다.
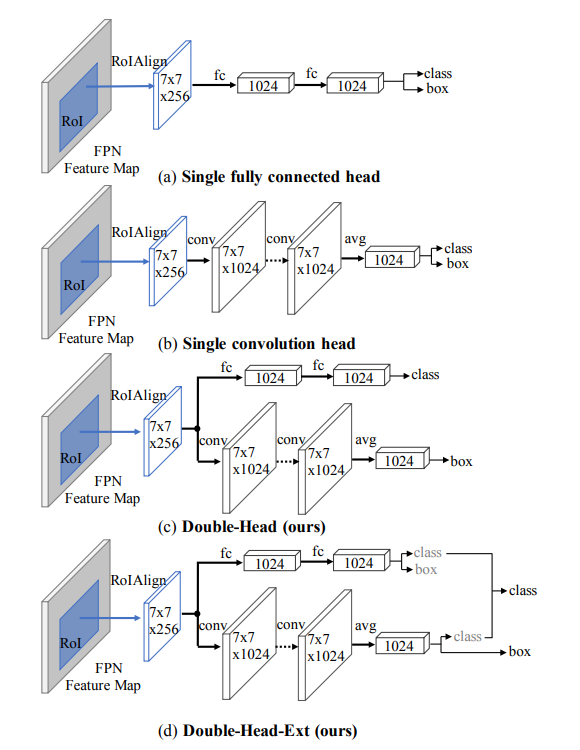
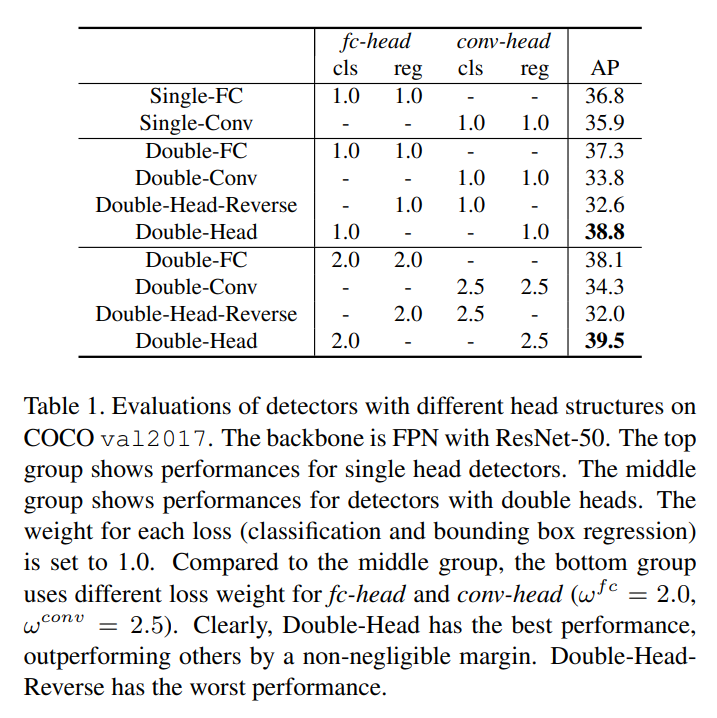
- 위의 그림에서 (c)와 같은 Double-Head 방법을 제시한다. fully-connected head는 classification에, convolution head는 bounding box regression에 초점을 두었다. 더나아가, (d)와 같이 conv-head의 classification과 fc-head의 bounding box regresssion과 같은 집중되지 않은 task를 활용하였다.
3. Related Work
- One-stage Object Detectors
- OverFeat: feature maps에 sliding windows를 사용
- SSD/YOLO: predicting object class and locations응 통해 tuned for speed
- RetinaNet: focal loss를 이용하여 극단적인 foreground-background class의 불균형을 해결
- Point-based methods(CornerNet, CenterNet, etc): key point estimation networks로 만들어짐
- Two-stage Object Detectors
- R-CNN: selective search에 의해 생성된 proposals로부터 추출된 features를 딥러닝을 적용
- SPPNet: spatial pyramid pooling 구조를 사용하여 RCNN의 속도를 증가
- Fast R-CNN: differentiable RoI Pooling 구조를 사용하여 speed와 performance를 향상
- Faster R-CNN: RPN 네트워크 사용
- R-FCN: translation-variance 문제를 해결하기 위해 position sensitive RoI pooling을 적용
- FPN: multiple layers에 있는 features를 추출하기 위해 lateral connection에 top-down 구조를 적용
4. Analysis: Comparison between fc-head and conv-head
- Data Processing for Analysis
- 공정한 비교를 위해서, RPN으로 proposal을 생성하는 대신에 predefined proposal을 생성하였다. predefined proposal은 서로 다른 사이즈의 ground truth box 주위에 sliding windows를 포함하고 있다.
- predefined proposal과 ground truth를 20개 bin으로 IoU를 나누고, proposals를 그룹핑하였다.
-
Comparison on Classification Task & Comparison on Localization Task
- Discussion
-
왜 fc-head는 classification score와 proposal IoU 사이에 상관관계를 보이고, localization에 성능이 더 안좋을까? 이러한 이유를 본 논문 저자들은 fc-head가 conv-head보다 공간적으로 sensiive하기 때문이라고 생각한다. 직관적으로, fc-head는 input feature map의 다른 위치에 공유되지 않은 transformation을 적용한다. 따라서 암묵적으로 공간정보가 깊숙이 있다는 것을 알 수 있다. fc-head의 spatial sensitivity는 객체를 구분하는데 도움을 줄 수 있다. 하지만, 전체 객체의 위치를 결정하는데는 불충분하다.
-
반대로, conv-head는 공유되는 transformation을 적용하기 때문에 input feature map에 모든 위치 정보가 있다.
-
5. Our Approach: Double-Head
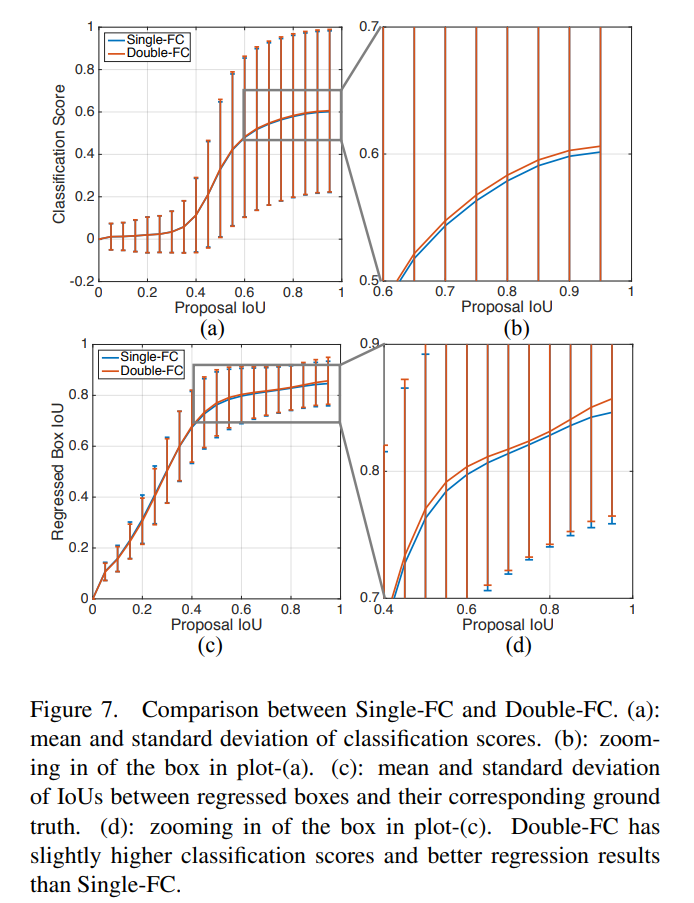
- 제안한 Double-Head 구조는 fully connected head가 classification, convolution head는 bounding box regression을 가지는 구조이다. 추가로, Double-Head-Ext는 fc-head의 bounding box와 conv-head의 classification과 같은 중심적이지 않았던 부분을 확장하였다.
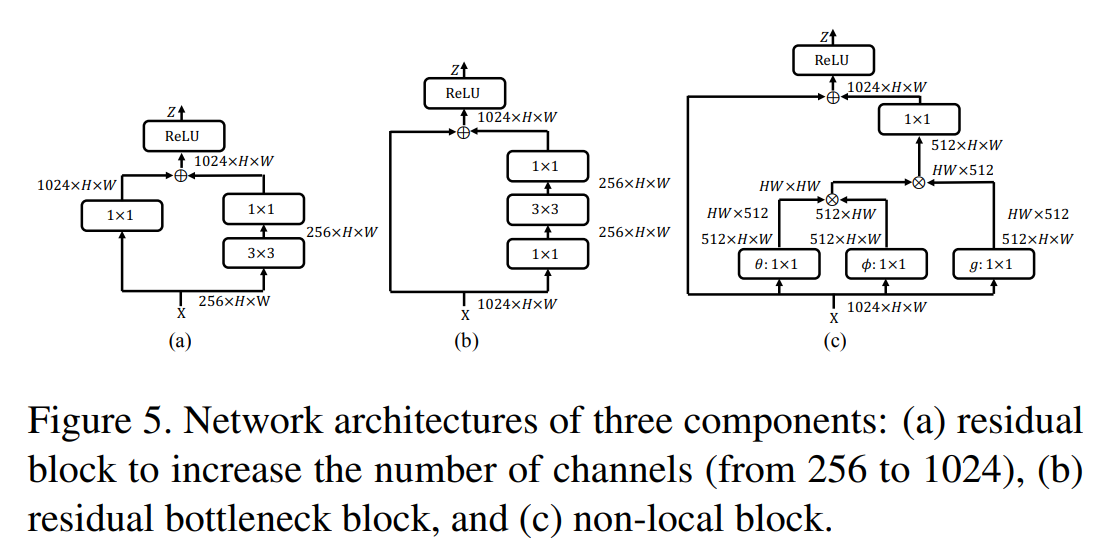
- 실험을 통해, 중심적이지 않았던 부분(fc-head의 bounding box regression과 conv-head의 classification)이 2가지 면에서 도움을 주었다.
-
(a) bounding box regression이 fc-head에서 auxiliary supervision을 제공해준다.
-
(b) 두 head의 classifier가 상호보완적이다.
-
- 그러므로 중심적이지 않았던 task의 supervision과 상호보완적인 fusion 메소드를 통해, inference 과정에서 두 head로부터 얻어진 classification 점수를 결합한다.
6. Experiment Result